Evolution and its Adversaries (Part-10)
Far from appearance of new species, mutations have been found to be actually degenerative. Of thousands, no experiment led to appearance of an advantageous trait. Since Darwinists had millions of years on their side, they could sit back and write the narratives. But some were not satisfied. They conducted experiments to induce mutation. No number of experiments led to any beneficial change, writes SYED IQBAL ZAHEER.
Any scientific theory that did not die out in ten years needs to be modified in the light of the latest data emerging from laboratories and research fields –so fast are the current developments in science. Evolutionary theory as presented by Darwin is more than a hundred and fifty years old. Its skeleton survival is made possible by atheist biologists who, when questioned, and cornered in arguments, challengingly demand an alternate theory that should deny any role to Divine powers. P.J. Bowler is quoted in The Independent Gene:
“There may be genuine scientific reason for suspecting that the synthetic theory [i.e. the modified theory of evolution: Au.] does not offer a complete explanation of evolution, but most biologists feel that the alternatives will only command their respect if they can be dissociated from the anti-Darwinians’ often one-sided pronouncements on moral issues.” (p. 221)
But, in truth, moral issues are a thin façade. The main concern is that if the scientists leave room for entry to an alternative theory, it is “God alone knows how and why” idea that will dominate. And, if that is allowed, religionists (with ghosts as their assistants) would enter with their wide and varied ideas, ideologies, notions, creeds and dogmas. They will be closely followed by saints (dead and alive), priests, holy men, ecclesiasts, spiritualists, soothsayers, and quacks of all kinds.
Unstoppable would be divination, magic, witchcraft, voodoo, and so forth. Soon modern man will be intellectually in caves and forests – a threat already looming. In fact, in some parts of the world, the ruling class appears to be re-establishing, quite successfully, this cultural ethos.

Science vs. Religion
Perhaps it would not be entirely inappropriate to point out at this juncture that Richard Dawkins fails to cite in his book “The God Delusion,” a single example of a non-scientific statement sanctioned by the Qur’an. He skirts away as dexterously from data that place a question mark before Darwinism, as he hides his personal opinion of Islam in the “Index” of his work “The Greatest Show on Earth – The Evidence for Evolution.”
The entry: ‘Islamic view of creation,’ in the Index of the book refers the readers to p.154. But the discussion there is about Harun Yahya’s biological errors; there is nothing, neither on this page nor on preceding and following pages, about Islamic viewpoint concerning creation.
There is yet another reference leading to pages 436-437 but which too offer nothing about ‘Islamic view on creation.’
Another entry in the “Index” under ‘Islamic view of evolution,’ leads to page 151 of the book. But, once again, the reference is entirely fanciful. There is no mention of ‘Islamic view of evolution’ on that page.
Yet again, on p. 106 Dawkins states:
“… some 40 percent of the American population, and a somewhat smaller percentage of the British population, claim to believe that the age of the Earth, far from being measured in billions of years, is less than 10,000 years. Lamentably, especially in America and over much of the Islamic world, some of these history-deniers wield power over schools and their syllabuses.”
This is a misleading statement. The prevalent belief about the age of the Earth, among the educated and uneducated of the Islamic world is: “We do not know.”It is Jewish and Christian idea that the earth was created 6000 years ago. Muslims do not subscribe to this view. The Judeo-Christian tradition traces nineteen generations between Adam and Abraham, each of whom has been named. But the Prophet (saws) has warned against the contents of Jewish/Christian literature, that they have been heavily doctored. Ibn `Abbas has said, “Whoever traced lineage beyond Adnan b. Udud lied.” And Adnan b. Udud lived some 400 years before the Prophet.
At all events, and the greatest show of inaccuracies apart, were Darwin to be alive today and present his biological ideas to the scientific community, he would be booed, ridiculed, and sent back to do some home-work before talking to an educated audience. Thousands of scientists have been generating tens of thousands of peer-reviewed papers, with newest of research results backed by countless experiments in the labs, checked and rechecked, in different parts of the world, resulting in piles upon piles of accumulating unchallengeable data, which refute almost every technical concept that Darwin used for his Origin of Species. To a scientific mind, the details of his theory sound like myth in scientific garb. It is taught in educational institutions as given: a set of doctrines that must be believed in, which may be questioned only at the risk of earning scorn, and draw the ire of biological churchmen and priests who pontifically pronounce that their theory has to be true, because it is true. Today, Darwinism is a dogma. You better subscribe to it, or you are ‘not of us.’ If you are in a research center, you are likely to be assigned to a project running at the basement.
The picture is well drawn by Perry Marshall. He writes,
“James Shapiro, who discovered Transposition in bacteria, said (during a talk at Fermilab in 2010): ‘There are piecemeal coding sequences, expression signals, splicing signals, regulatory signals, epigenetic formatting signals, and many other DNA elements … that participate in the multiple functions involved in genome expression, replication, transposition, repair and evolution.’
“After the talk a small group huddled around him (and one of them asked), ‘You mean the mutations aren’t random?’
‘No sir,’ replied Dr. Shapiro, ‘they’re not random at all. When bacteria are comfortable, some mutations cannot be found in over ten billion cells. But when they’re starving, the mutation frequency can go by a factor of >100,000-fold and they develop new adaptations so they can survive.’
I watched the face of the man questioning Dr. Shapiro. You could almost hear the gears grinding inside his head! The man looked to be in fifties; I imagine he had bought into the random mutation myth decades ago and had never questioned it since.” (Evolution 2, p.88-89)
Random Mutation
Primarily, there are two kinds of mutations: genetic and chromosol. Also referred as ‘point mutation,’ genetic mutation takes place at the genetic level, usually in the alteration of nucleotides resulting in wrong amino acids being coded.
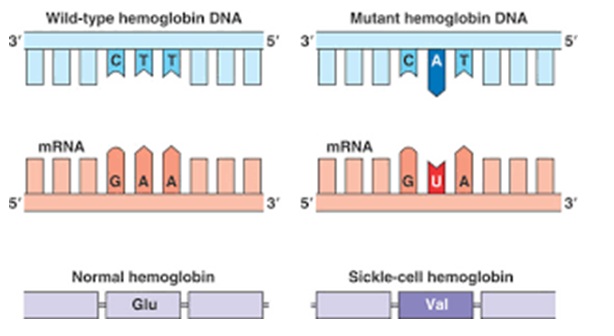
Fig. 10-1: The above is an example of ‘point mutation.’ Looking at the figure on the left side, it can be noticed in the upper strip that the nucleotides CTT perfectly match with GAA of the lower strip. As a result, it gives rise to a normal amino acid called Glutamine (Glu).
However, for some reason the situation changed in the figure on the right side during copying. What was CTT became CAT in the upper strip, and what was GAA became GUA in the lower strip. It is a case of mismatch. If the ‘DNA Repair’ machine did not detect, and did not correct the error, the alteration (mutation) would lead to the formation of an amino acid called Valine (Val). This change will result in the formation of a wrong protein, which would in turn lead to a disease called Sickle-cell Hemoglobin.
Margulis: “Many ways to induce mutations are known but none lead to new organisms. Mutation accumulation does not lead to new species or even to new organs or to new tissues … Even professional evolutionary biologists are hard put to find mutations, experimentally induced or spontaneous, that lead in a positive way to evolutionary change.” (Evolution 2, p. 72, Perry Marshall, BenBella Books, 2013)
The other type of mutation takes place at the chromosol level when a short or long strip of the DNA is shifted from one location to another within a chromosome, or, from one chromosome to another.
“Genetic recombination causes major rearrangements of the genome with surprising frequency: the genome can expand or contract by duplication or deletion, and its parts can be transposed from one region to another to create new combinations.”(Molecular Biology of the Cell, p. 735, epub)
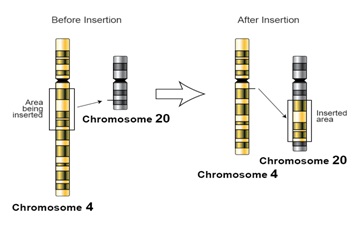
Fig. 10-2: An illustration of chromosol mutation. In this case, a chunk of the Chromosome 4 is sliced off from it and is inserted into Chromosome 20. Their altered figures are shown on the right side. Most of the times, such a mutation is lethal.
At all events, our point is that biologists now on the scene are showing that random mutation as a basis for appearance of new traits and of new species is turning out to be a myth. But it is not the only myth around. The entire Theory of Evolution, both the classical as well as its new format (called the Synthetic Theory) are gradually turning into myths. But doctrines die hard; especially in this case, when the priests are scientists – although now, as with every priest of a false religion, there is a question mark before the intellectual integrity of these newest priests.
We have, in the past pages largely demonstrated why, according to several biologists, the theory of evolution is now falling into disrepute. Their rejection is based on latest data emerging from research works. In contrast, biologists defending the theory have not relied on hardcore, coherent data, but rather, bits and pieces stitched together, and on interpretations which in any case are quite off the mark. These modern neo-Darwinians always avoid concrete details, and are especially poor on citations from latest research works. For instance, whole books have been written, supported by dozens of scientific articles in respected science magazines, which claimed that ninety-six percent of human DNA is junk. They explained it as the left-over of past species from which man has appeared. This junk was, according to them, inherited through generations, species to species, which proves beyond a shadow of doubt that humans are from chimpanzees, they from lower order animals, and so on down the line until you arrive at the ‘great grandfather,’ the amoeba. The argument was quite convincing. But now, evidence is fast emerging that far from junk, the DNA strips that seemed to be functionless, so-called garbage of the past carried into the present, are so essential that if removed from the DNA chains, a new life cannot be developed. The argument fails but is never acknowledged.
There isn’t any pillar of classical Darwinism, as well as its modern version called the Synthetic Theory, that has not been felled by modern research. In the following pages we shall present research results that stand against the assumptions of the evolutionists.
“Consider the process by which a new anatomical feature – say, an elongated beak – appears in the course of evolution. A random mutation occurs that changes the amino acid sequence of a protein or the timing of its synthesis and hence its biological activity. This alteration may, by chance, affect the cells responsible for the formation of the beak in such a way that they make one that is longer. But the mutation must also be compatible with the development of the rest of the organism; only then will it be propagated by natural selection. There would be little selective advantage in forming a longer beak if, in the process, the tongue was lost or the ears failed to develop. A catastrophe of this type is more likely if the mutation affects events occurring early in development than if it affects those near the end. The early cells of an embryo are like cards at the bottom of a house of cards -a great deal depends on them, and even small changes in their properties are likely to result in disaster.
“Fundamental steps appear to have been “frozen” into developmental processes, just as the genetic code or protein synthesis mechanisms have become frozen into the basic biochemical organization of the cell. In contrast, cells produced near the end of development (or produced early but forming accessory structures such as the placenta that are not incorporated in the adult body) have more freedom to change. It is presumably for this reason that the embryos of different species so often resemble each other in their early stages and, as they develop, seem sometimes to replay the steps of evolution.”(Bruce Albert & others, Molecular Biology of the Cell, P. 62, epub)
The above is not in denial of evolution; but demonstrates that a single ‘random mutation’ cannot lengthen a bird’s beak. Several other ‘random mutations’ must simultaneously occur before a beak is elongated, such as, to name a few, elongation of the tongue, the muscles around, modification of the neck to support the longer beak, and a host of other changes. Consider the following from the same famous text book:
“One of the most impressive features of DNA replication is its accuracy. Several proofreading mechanisms are used to eliminate incorrectly positioned nucleotides; as a result, the sequence of nucleotides in a DNA molecule is copied with fewer than one mistake in 109 nucleotides added.
“Very rarely, however, the replication machinery skips or adds a few nucleotides, or puts a T where it should have put a C, or an A instead of a G. Any change of this kind in the DNA sequence constitutes a genetic mistake, called a mutation, which will be copied in all future cell generations since “wrong” DNA sequences are copied as faithfully as ‘correct’ ones. The consequence of such an error can be great, for even a single nucleotide change can have important effects on the cell, depending on where the mutation has occurred.” (Ibid, p. 101)
Stephen Mayer notes in his “Darwin’s Doubt”:
“University of the Georgia geneticist John McDonald notes a conundrum: The results of the last twenty years of the research on genetics basis of adaptation has led us to a great Darwinian paradox. (Genes) that are obviously variable within natural populations do not seem to lie at the basis of many major adaptive changes, well those (genes) that seemingly to constitute that foundation of many, if not most, major adaptive changes apparently are not variable within natural populations.
“Australian evolutionary geneticist George Miklos puzzles over the usefulness of Darwinism: What then does this all encompassing theory of evolution predict? Given a handful of postulates, such as random mutations, and selection coefficients, it will predict changes in (genes) frequencies over time. Is this what a grand theory of evolution ought to be about?
“Jerry Coyne, of the Department of Ecology and Evolution at the University of Chicago, arrives at an unanticipated verdict: We conclude __ unexpectedly __ that there is little evidence for the neo-Darwinian view: its theoretical foundations and the experimental evidence supporting it are weak.
“And University of California geneticist John Endler ponders how beneficial mutations arise: Although much is now about mutation, it is still largely a “black box” relative to evolution. Novel biochemical functions seem to be rare in evolution, and the basis for their origin is virtually unknown. (Michale Behe, Darwin’s Black Box, p. 28-29)
And,
As Susumo Ohno has explained: Assuming a spontaneous mutation rate to be a generous 10–9 per base pair per year . . . it still takes 10 million years to undergo 1% change in DNA base sequences. It follows that 6–10 million years in the evolutionary time scale is but a blink of an eye. The Cambrian explosion . . . within the time span of 6–10 million years can’t possibly be explained by mutational divergence of individual gene functions. (Debating Design, p. 378, William A. Dembski and Michael Rose, Cambridge, 2006).
Genes and their Functions
Much of the evolutionary thought of the past century centered around genes. Genes were supposed to carry in coded language all the information about biological organisms. In case of man, there was everything there that you could ask for to build a new body, except of course, you wouldn’t know how to ingest life. The gene-carrying DNA was like a blueprint for a building. Given the raw material, a builder would know how to construct the building: the organism. A man was what his genes were. From the thickness of his hair to the size of the limbs, he was determined by the genes.
And the genes were unbeatable masters who had their way. Their objective was single: replicate, replicate, replicate. Although blind, they were selfish. Yet, sitting in a dark room called the nucleus, they were omniscient. They knew what was happening within the cell, outside the cell within the body, and all about their surrounding: whether the wind was blowing or not (for cotton seeds to fly away: Dawkins), whether there was enough food available or not, whether there were few competitors or many, whether predators were lurking around or not, if yes, then should they outsmart them by changing body-color, or prepare for an electrical shock, or seek the help of poisonous sting, or simply release pungent odor that would turn away the predator in disgust. Examples were quoted from the living world.
And genes had it all. In fact, the prime objective of human genome sequencing project completed early this century was to help identify genes that were responsible for diseases like cancer, tuberculosis, diabetes, and so forth. In the words of David Moore who quotes Mann:
“The pattern continued into the 1980s with scientific reports linking reading disability to genes on chromosome 15, schizophrenia to chromosome 5, psychosis to chromosome 11, and manic depression to chromosome 11 and the X chromosome. All were announced with great fanfare; all were greeted unskeptically in the popular press, all are now in disrepute.” (The Dependent Gene, p. 243)
The scientific predictions failed when the sequencing of the entire genome was completed, there was no indication that the genes were responsible for the life threatening diseases. With the arrival of more and more data, old notions had to be set aside. Genes were found to be not doing much of what was thought they were single-handedly doing.
Again, against the notion given by some biologists, genes do not do any self-replication either. Genetic-message carrying nucleotides are sitting on the chromosomes. A machinery arrives that straitens up the coiled chromosome, another machine pries open it, yet another (actual several) arrive to read the nucleotide molecules … and so on, until a new copy is produced. In this process of gene-copying, genes themselves have no role to play. They are subjected to replication, and do not replicate. Nor do they order the replication. The work is done on them. They do no work.
But the claim by the evolutionist was that it was at the genetic level that the evolutionary power worked. The main factor was ‘mutation’ which was alteration of molecules on DNA, called nucleotides, some three billion of them.
According to evolutionists, accidental changes by radiation or like factors altered the chemical codes that created new traits in physical bodies. Natural selection then took over allowing for the survival of the fittest and destroying erroneous changes made by mutation. The alterations, in turn, when accumulated and inherited, from generation to generation, gave rise to new species – again through the power of natural selection. The alteration to the genetic code by random mutation was entirely accidental, but which always proved to be directional and creative. The changes gave such directions as to allow for the appearance of new species. This was accomplished by Natural Selection. (To some rationalists: natural selection is a ghost).
But in actual fact, no such thing happens. Far from appearance of new species, mutations have been found to be actually degenerative. Of thousands, no experiment led to appearance of an advantageous trait. Since Darwinists had millions of years on their side, they could sit back and write the narratives. But some were not satisfied. They conducted experiments to induce mutation. No number of experiments led to any beneficial change. But rather new actors appeared. It was also discovered that genes do supply the information in code, but they were never acting alone. There were other factors that decided how a body would develop. We shall discuss some of these factors in the forthcoming issue, Allah willing.
(To be continued)

