What is the Brain?

The brain is the center of the nervous system in animals. All vertebrates and the majority of invertebrates have a brain. Some “primitive” animals such as jellyfishes and starfishes have a decentralized nervous system without a brain, while sponges lack any nervous system at all.
In vertebrates, the brain is located in the head, protected by the skull and close to the primary sensory apparatus of vision, hearing, balance, taste, and smell. The human brain appears to have no localized center of conscious control. The brain seems to derive consciousness from the interaction among numerous systems within the brain.
The human brain controls the central nervous system by way of the cranial nerves and spinal cord, the peripheral nervous system and regulates virtually all human activity. The brain is made up of over 100 billion nerve cells with each brain cell connected to around 10,000 other cells, which equals around 1000 trillion connections in your brain. Your brain is actually very soft, jelly-like, and not gray but a deep red in color.
The brain controls both involuntary, or “lower,” actions, such as heart rate, respiration, and digestion. Complex, or “higher,” mental activity, such as thought, reason, and abstraction, is consciously controlled.
Brain Facts and Figures
 How long is the spinal cord and how much does it weigh?
How long is the spinal cord and how much does it weigh?
The average spinal cord is 45 cm long in men and 43 cm long in women. The spinal cord weighs approx. 35 grams.
How much does the brain weigh?
The human brain weighs on average three pounds or 1.5 kg.
What size is an adult human’s brain?
The human brain is about the size of a cantaloupe.
Average brain width = 140 mm
Average brain length = 167 mm
Average brain height = 93 mm
How much oxygen does the brain need to stay “conscious”?
An adult’s brain requires around 20% of the body’s oxygen.
How much blood is needed by the brain?
Approximately 20% of the blood flowing from the heart is pumped to the brain. The brain needs constant blood flow in order to keep up with the heavy metabolic demands of the neurons.
What is the largest part of the brain?
The biggest part of the brain is the cerebrum which makes up 85% of the brain’s weight. The cerebrum is the thinking part of the brain and it controls your voluntary muscles.
Does the brain work at the Speed of Light?
No, far from it. Axons, the long output connection from a cell, come in two types: myelinated and unmyelinated. Myelinated axons have an extra layer of “insulation,” a fatty substance, which allows the impulse to travel about 10 to 100 meters per second (36,000 km/hr). Unmyelinated axons only transmit at about 1 meter per second. When the signal reaches the end, it has to cross the synapse to influence the next cell, which adds about 5 ms. 10 meters per second = 22.356 mph and 100 meters per second = 223.561 mph. As you can see it is a lot slower than the speed of light in a vacuum which is exactly 299,792,458 meters per second, or 186 000 miles per second, or 670,616,629 mph.
Further Questions and Answers on the Brain
What are studies of the brain called?
The study of the brain and its functions is known as neuroscience. Psychology is the scientific study of the mind and behavior. Neurophysiology is the study of normal healthy brain activity. Neurology and psychiatry are both medical approaches to the study of the mind and its disorders and pathology or mental illness respectively.
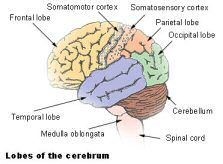
How many main parts of the brain are there?
 The human brain can be divided into three main parts: the forebrain, midbrain, and hindbrain:
The human brain can be divided into three main parts: the forebrain, midbrain, and hindbrain:
1) The forebrain includes the several lobes of the cerebral cortex that control higher functions.
2) Midbrain functions include routing, selecting, mapping, and cataloging information, including information perceived from the environment and information that is remembered and processed throughout the cerebral cortex.
3) Hindbrain – (Rhombencephalon) is a developmental categorization of portions of the central nervous system in vertebrates. A rare disease of the rhombencephalon, “rhombencephalon synapsis” is characterized by a missing vermis resulting in a fused cerebellum. Patients generally present with cerebellar ataxia.
What is a neuron?
A neuron is a nerve cell in the brain. The human brain is made up of approximately 100 billion (100,000,000,000) neurons.
Is the brain an organ?
The brain is an organ as it controls the functions of the body. It is sometimes referred to as a muscle of thinking as the brain actually tells your muscles what to do. The brain is the most important organ in the body because it controls all of the bodily functions as well as the other organs.
Do men have a larger brain than women?
Male humans have a 10% larger brain than females. A study of 46 adults aged 22-49 years found an average brain volume of 1273.6cc for men, ranging from 1052.9 to 1498.5cc, and 1131.1cc for women, ranging from 974.9 to 1398.1cc. However, differences in male and female brain weight and size do not mean differences in mental ability. There is evidence of a gradual increase in average brain size over the last centuries, estimated to have been around 0.5% per decade.
Is a computer smarter than a human brain?
The brain has a processing capacity of 0.1 quadrillion instructions per second. The fastest supercomputer in the world, called Roadrunner is capable of handling 1.026 quadrillion calculations per second. However, the computational power of the human brain is difficult to ascertain, as the human brain is not easily paralleled to the binary number processing of computers. For while the human brain is calculating a math problem, it is subconsciously processing data from millions of nerve cells that handle the visual input of the paper and surrounding area, the aural input from both ears, and the sensory input of millions of cells throughout the body. The brain is also regulating the heartbeat, monitoring oxygen levels, hunger and thirst requirements, breathing patterns and hundreds of other essential factors throughout the body. It is simultaneously comparing data from the eyes and the sensory cells in the arms and hands to keep track of the position of the pen and paper as the calculation is being performed.
Can an adult grow more brain cells?
A landmark study in late 1998 by researchers from Sweden and the Salk Institute in La Jolla, California, showed for the first time that some brain cells in mature humans may regenerate under certain circumstances.
Do humans only use 10% of the brain?
No, we use all of our brains.
What are Neurodegenerative diseases?
Neurodegenerative diseases, such as Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, motor neurone disease, and Huntington’s disease are caused by the gradual death of individual neurons, leading to decrements in movement control, memory, and cognition.
Does alcohol kill brain cells every time you drink?
The idea that alcohol kills brain cells has long been promoted. Drinking alcohol does not actually “kill” brain cells. Roberta Pentney, professor of anatomy and cell biology at the University at Buffalo, concludes that alcohol does not kill brain cells but it damages the dendrites, the branched ends of nerve cells that bring messages into the brain cell causing damage to the way the cells in the brain communicate. Luckily the damage is largely reversible and not permanent. However, years of alcohol abuse can cause serious neurological damage, including Wernicke-Korsakoff syndrome.
In what part of the brain do you get brain tumors?
Brain tumors are classified depending on the exact site of the tumor, the type of tissue involved, benign or malignant tendencies of the tumor, and other factors. Primary (true) brain tumors are commonly located in the posterior cranial fossa in children and in the anterior two-thirds of the cerebral hemispheres in adults, although they can affect any part of the brain.
How are memories stored and retrieved?
Unfortunately, we don’t yet comprehend exactly how this happens or how memories are recalled years later for retrieval.
(To be concluded)

